|
Performance Characterization and Modelling of Scientific Workflows in Large Scale Distributed Computing Environments like Grid
Summary:
Today’s scientific work is converging to electronic science (e-science) and the field of “scientific applications” has already emerged. The scientific applications are usually complex – composed of a set of coordinating tasks with complex dependencies among them (referred as workflow applications) – and require high performance computing infrastructure (HPC) for their execution. The centralized HPC infrastructures are expensive to buy and maintain for individuals/ individual organizations. Grid computing enables individuals/organizations to share their resources and aggregate shared resources to form a cheaper HPC infrastructure. Such sharing and use of the resources has to be effectively managed by the resource owners and the scientific application users respectively. Both of them require application performance estimates (obtained through performance models) to manage their resources and time. However, modelling performance of scientific workflow applications is complex due to their complex structures and heterogeneity and dynamic behavior of the shared resources. In the proposed study, we plan to characterize the performance of scientific application in the Grid (as a cheap source for HPC) and identify important attributes defining their performance. We also plan to develop automatic methods employing machine learning techniques to model the overall performance of scientific workflow applications in distributed and shared environment of the Grid. This will greatly help the scientific application user for planning execution of their applications and the resource owners/administrators for managing usage of their resources. In addition, the application performance modeling service will also provide a decisive base to the key decision making services (like resource broker, task scheduler, performance steering service etc.) in the Grid environment.
System Architecture
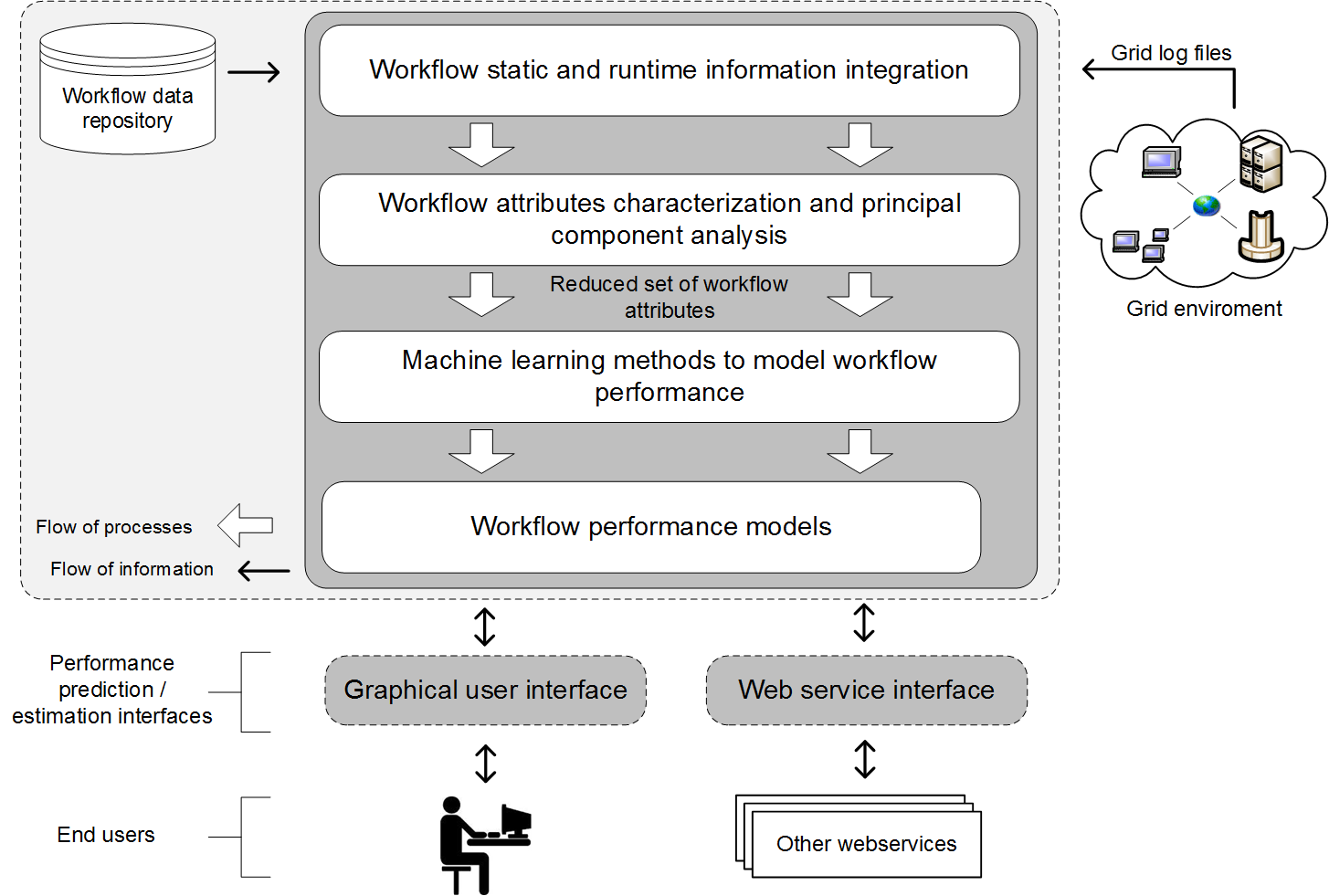
Figure: System Architecture
Project Accomplishments and Results
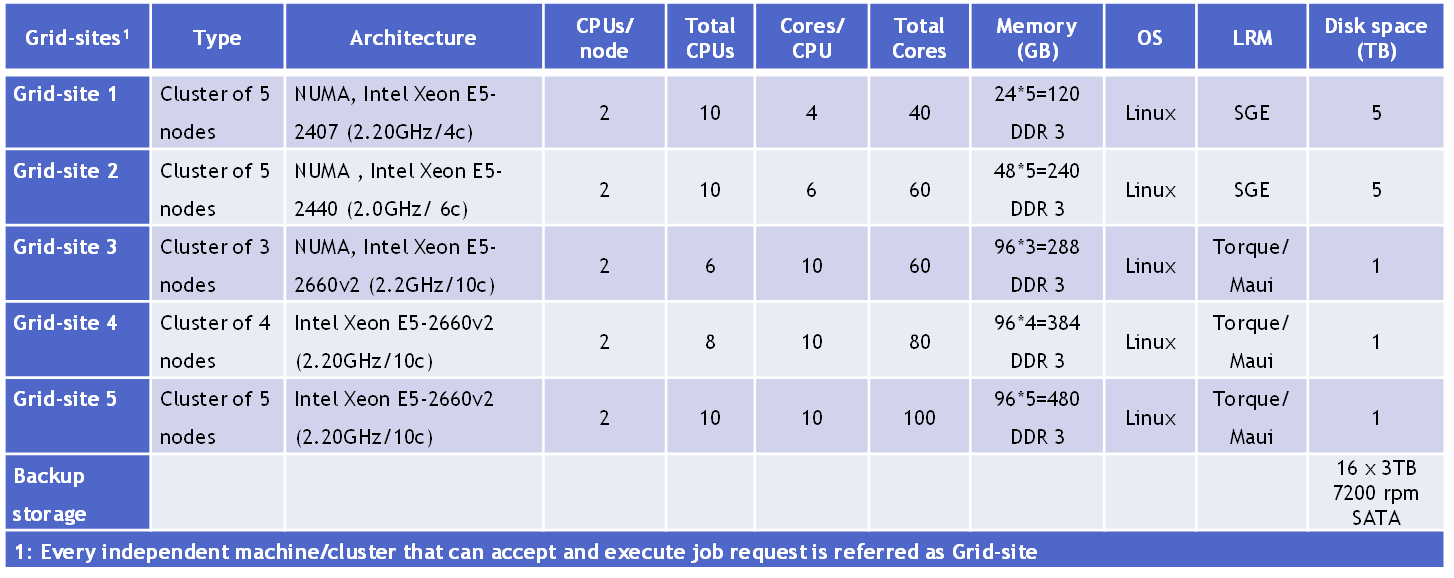
HPC Grid Infrastructure for research and training purposes for all KAU faculty and students.
TABLE: Developed Grid Infrastructure
Grid Servers
Broader Impacts of the Project
- Promotion of research culture at KAU.
- Increased motivation among KAU scientists for porting their traditional scientific applications to HPC platform.
- Driving collaborations between FCIT and other departments by providing them computing facilities.
- Trained students for HPC usage and applications.
Benefits to the Kingdom
The project outcomes benefit the Kingdom in four major ways.
- First, it has developed a local Grid setup in the computer labs of Faculty of Computing and Information Technology (FCIT), King Abdul Aziz University, Jeddah. This setup not only benefits the current project, but will also serve as a basic infrastructure for students and faculty of KAU to get hands on experience of working on a distributed high performance computing infrastructure.
- Second, this will serve as a platform for adaptability of scientific workflow applications from other departments like material science, chemistry, biology etc.
- Third, the local students/administrators (involved in project) will be trained to work in the field of high performance computing environments like Grid. Such trained personnel will be helpful in initiating work in this domain and port classical scientific workflow applications to high performance computing environments.
- Last but not the least, this will be used to offer new courses in the domain of distributed and parallel computing / High performance computing / Grid computing.
|
Last Update
1/28/2019 9:13:28 AM
|
|
|
|